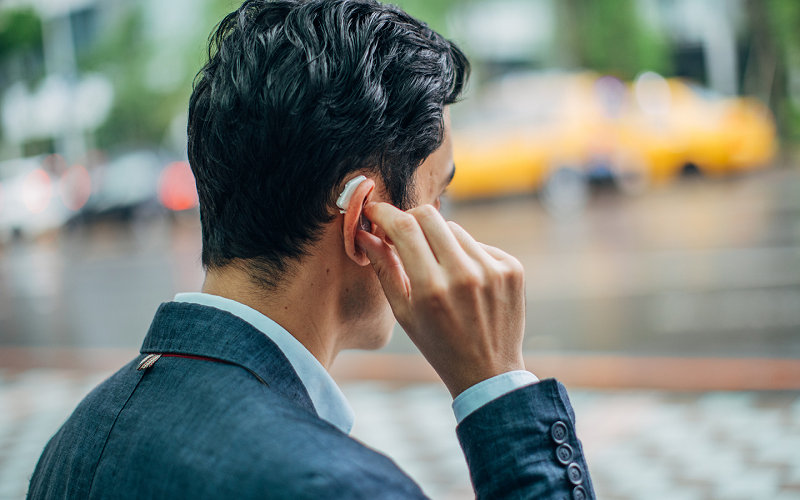
Hearing aids are vital tools that assist people with hearing loss in living their daily lives with clarity and confidence. Hearing aid batteries are important to these devices’ performance, as they power the amplification and signal processing functions required for better hearing. In this detailed tutorial, we will look at the many types of hearing aid batteries, their lifespan, and important maintenance advice to maintain the best performance from your Phonak hearing aid or any other brand.
1. Different Types of Hearing Aid Batteries.
Hearing aid batteries are available in four standard sizes, each distinguished by a unique colour code:
- Size 10 (Yellow)
- Size 13 (Orange)
- Size 312 (Brown)
- Size 675 (Blue)
The battery size required is determined by your hearing aid model’s size and power requirements. Size 10 batteries are typically used in smaller, more discreet hearing aids, although bigger devices may require size 13, 312, or 675 cells for more power and performance.
2. Zinc-Air vs. Disposable Batteries
The bulk of current hearing aid batteries are zinc-air batteries, which use oxygen from the air to start the chemical reaction required for power generation. These batteries often include a sticker tab that must be removed to allow air to enter and activate the battery. Once the tab is removed, the battery discharges and cannot be resealed.
Disposable batteries, on the other hand, are sealed devices that activate without the presence of air. Once drained, disposable batteries are discarded and replaced with new ones.
3. Lifespan and Storage Considerations
The longevity of hearing aid batteries varies according to battery size, hearing aid power consumption, and individual usage patterns. In general, smaller batteries (size 10 and 312) have a lower lifespan than larger ones (size 13 and 675).
To extend the life of your batteries, keep them in a cool, dry area at room temperature. Avoid exposing batteries to high heat or humidity since this can speed up discharge and lower overall performance. To avoid early activation and depletion, keep the sticker tab on zinc-air batteries until they are ready to use.
4. Change Batteries
Knowing when to replace your hearing aid batteries is critical for continued hearing aid use. Most hearing aids have low-battery indications, such as beeps or tones, to inform users when the battery is going low. Additionally, certain devices may emit warning sounds or provide battery condition indications on the device itself.
When replacing batteries, use clean, dry hands to avoid contamination or moisture damage. Insert the new battery into the battery compartment with the correct polarity (+ and -) as specified, ensuring a secure fit for best contact and performance.
5. Recycling and Disposal
Proper disposal of hearing aid batteries is critical for reducing environmental effects and ensuring safe handling of hazardous chemicals. Many local pharmacies, hearing care clinics, and electronics merchants have battery recycling schemes where you may send off unwanted batteries for safe disposal. Furthermore, several hearing aid manufacturers offer mail-in recycling schemes for spent batteries, allowing customers to return depleted batteries for proper recycling and disposal.
6. Ensure Compatibility with Phonak Hearing Aids
When ordering replacement batteries for a Phonak hearing aid or any other brand, make sure they are compatible with your specific device type. Phonak has a variety of hearing aid models with variable power requirements, so choosing the right battery size and type is critical for peak performance.
To establish the appropriate battery size and type, see your hearing healthcare expert or your Phonak hearing aid’s user handbook. Using the correct batteries will help your Phonak hearing aid last longer and work more consistently.
Conclusion
Hearing aid batteries power the amplification and signal processing capabilities of hearing aids, allowing people with hearing loss to communicate and engage effectively in their daily lives. Users may maintain optimal performance and longevity of their Phonak or other brand hearing aids by learning the many types of hearing aid batteries, their lifespan, and key maintenance suggestions. Remember to handle, store, and dispose of batteries safely to reduce environmental effects and preserve safe use practices.











+ There are no comments
Add yours